Notes for Machine Learning Data Lifecycle in Production (MLOps2) on Coursera/Deeplearning.ai
Week1
Introduction to Machine Learning Engineering in Production
Managing the entire life cycle of data
- Labeling
- Feature space coverage
- Minimal dimensionality
- Maximum predictive data
- Fairness
- Rare conditions
Modern software development
Accounts for:
- Scalability
- Extensibility
- Configureation
- Consistency & reproducibility
- Safety & security
- Modularity
- Testability
- Monitoring
- Best practice
Production machine learning system
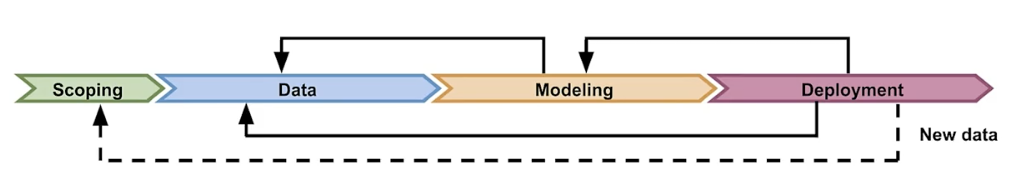
Challenges in production grade ML
- Build integrated ML systems
- Continuously operate it in production
- Handle continuously changing data
- Optimize compute resource costs
Production ML infrastructure
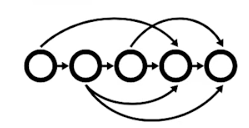
Directed acyclic graphs
- A directed acyclic graph (DAG) is a directed graph that has no cycles
- ML pipeline workflows are usually DAGs.
- DAGs define the sequencing of the tasks to be performed, based on their relationships and dependencies.
Pipeline orchestration frameworks
- Responsible for scheduling the various components in an ML pipeline DAG dependencies
- Help with pipeline automation
- Examples: Airflow, Argo, Celery, Luigi, Kubeflow
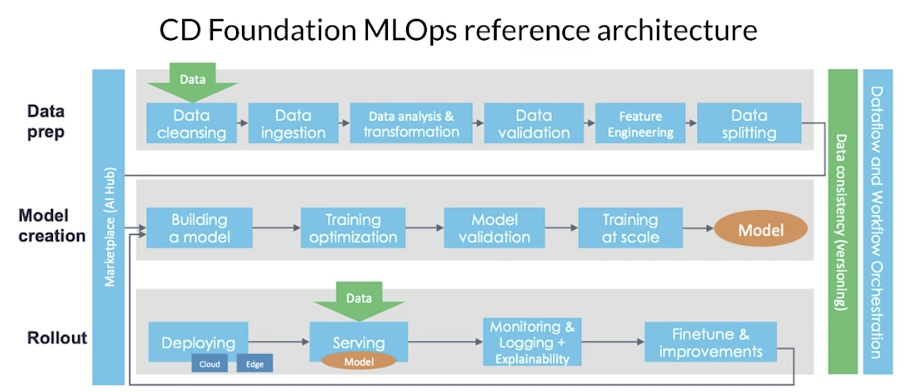
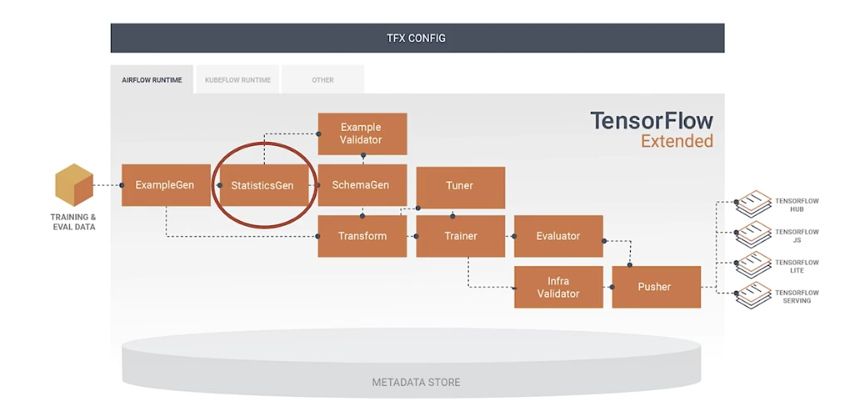
TensorFlow Extended (TFX)
End-to-end platform for deploying production ML pipelines.

Sequence of components that are designed for scalable, high-performance machine learning tasks.
TFX production components
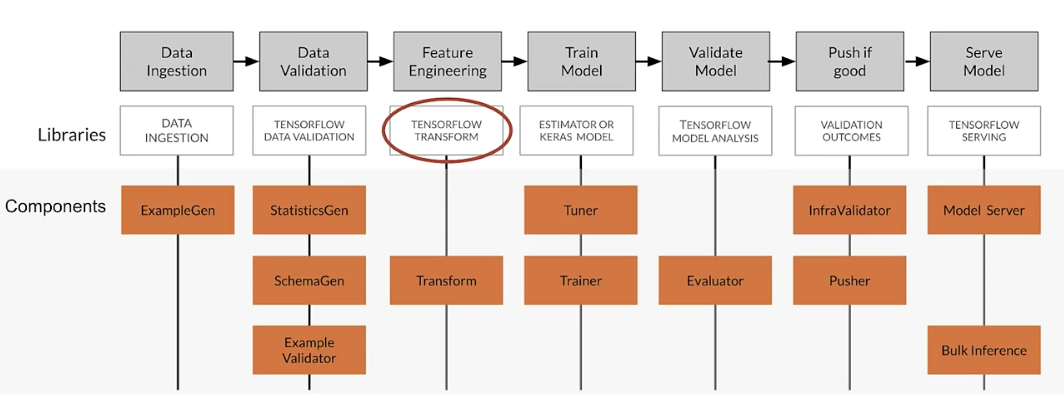
TFX Hello World
Key points
- Production ML pipelines: automating, monitoring, and maintaining end-to-end processes
- Production ML is much more than just ML code
- ML development + software development
- TFX is an open-source end-to-end ML platform
Collecting Data
ML: Data is a first class citizen
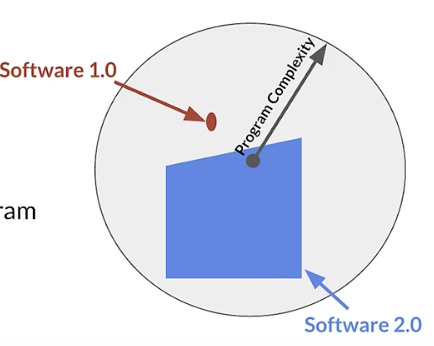
Software 1.0
- Explicit instructions to the computer
Software 2.0
- Specify some goal on the behavior of a program
- Find solution using optimization techniques
- Good data is key for success
- Code in Software = Data in ML
Everything starts with data
- Models aren’t magic
- Meaningful data:
- maximize predictive content
- remove non-informative data
- feature space coverage
Data pipeline
Data collection and monitoring
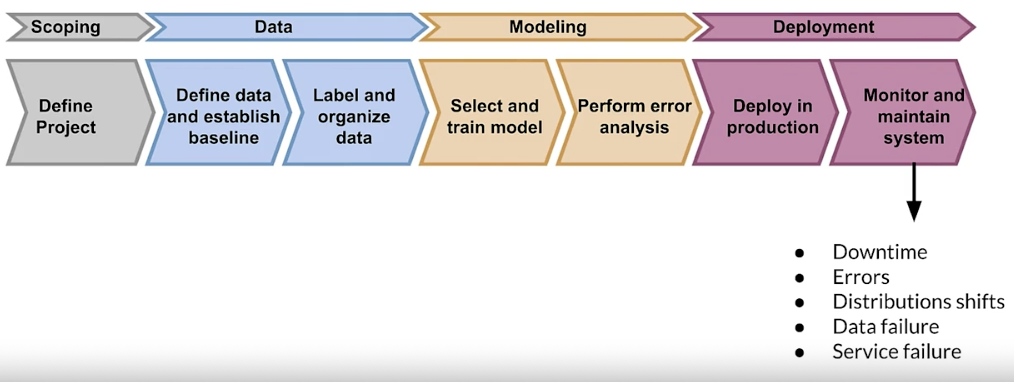
Key points
- Understand users, translate user needs into data problems
- Ensure data coverage and high predictive signal
- Source, store and monitor quality data responsibly
Example application: suggesting runs
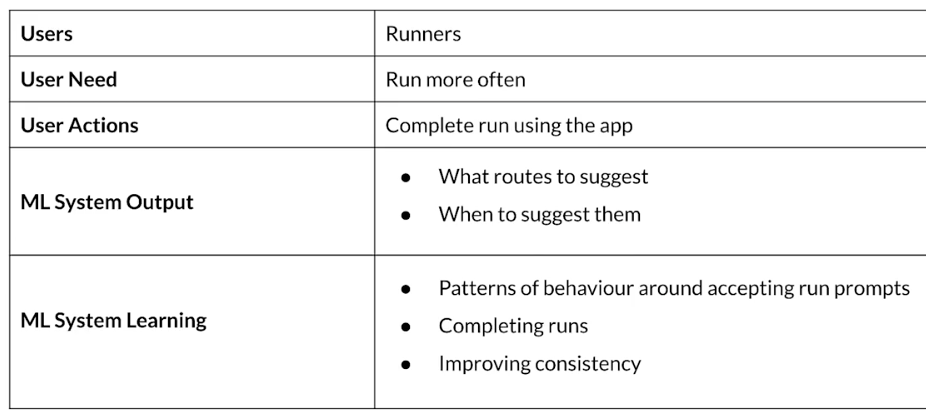
Key considerations
- Data availability and collection
- What kind of /how much data is available?
- how often does the new data come in?
- Is it annotated?
- If not, how hard/expensive is it to get it labeled?
- Translate user needs into data needs
- Data needed
- Features needed
- Labels needed
Example dataset
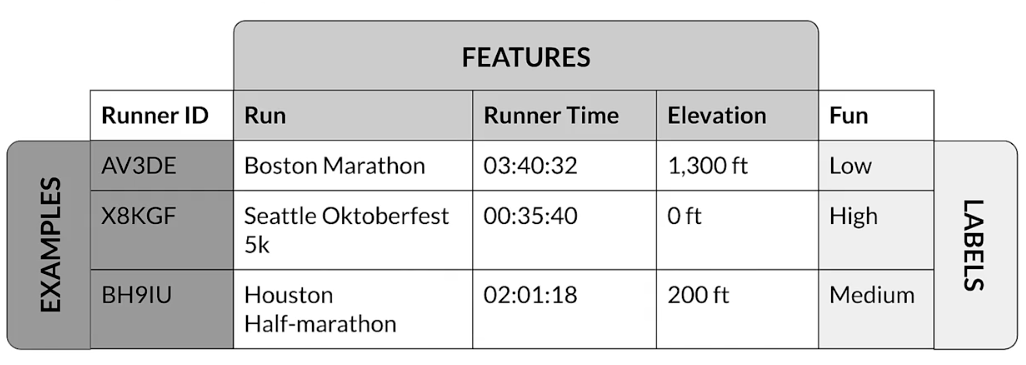
Get to know your data
- Identify data sources
- check if they are refreshed
- Consistency for values, units, and types
- Monitor outliers and errors
Dataset issues
- Inconsistent formatting
- Is zero ‘‘0", “0.0”, or an indicator of a missing measurement
- Compounding errors from other ML models
- Monitor data sources for system issues and outages
Measure data effectiveness
- Intuition about data value can misleading
- Which features have predictive value and which ones do not?
- Feature engineering helps to maximize the predictive signals
- Feature selection helps to measure the predictive signals
Translate user needs into data needs


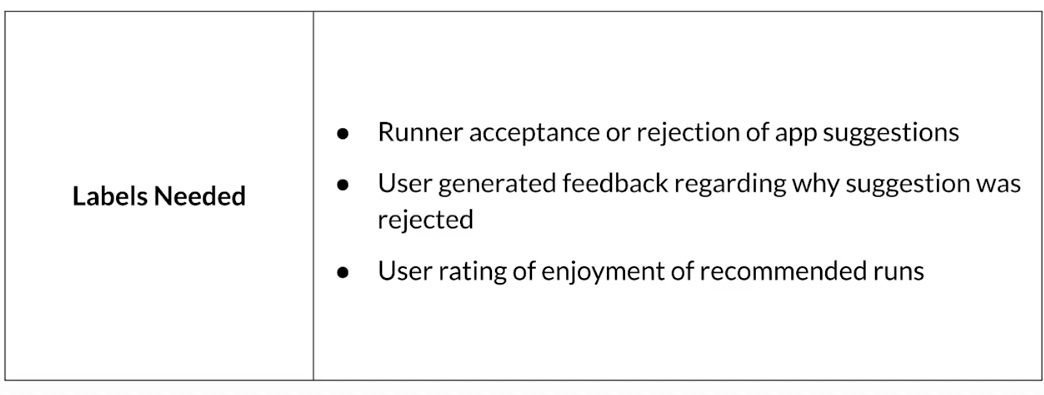
Key points
- Understand your user, translate their needs into data problems
- What kind of / how much data is available
- What are the details and issues of your data
- What are your predictive features
- What are the labels you are tracking
- What are your metrics
Avoiding problematic biases in datasets
Source data responsibly
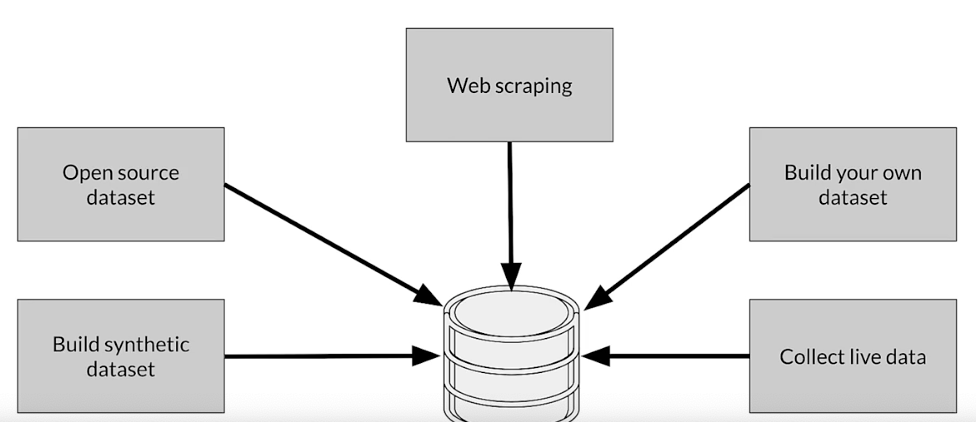
Data security and privacy
- Data collection and management isn’t just about your model
- Give user control of what data can be collected
- Is there a risk of inadvertently revealing user data?
- Compliance with regulations and policies (e.g. GDPR)
Users privacy
- Protect personally identifiable information
- Aggregation - replace unique values with summary value
- Redaction - remove some data to create less complete picture
How ML systems can fail users
- Representational Harm
- Opportunity denial
- Disproportionate product failure
- Harm by disadvantage
Commit to fairness
- Make sure your models are fair
- Group fairness, equal accuracy
- Bias in human labeled and/or collected data
- ML models can amplify biases
Reducing bias: design fair labeling systems
- Accurate labels are necessary for supervised learning
- Labeling can be done by:
- Automation (logging or weak supervision)
- Humans (aka “raters”, often semi-supervised)
Types of human raters
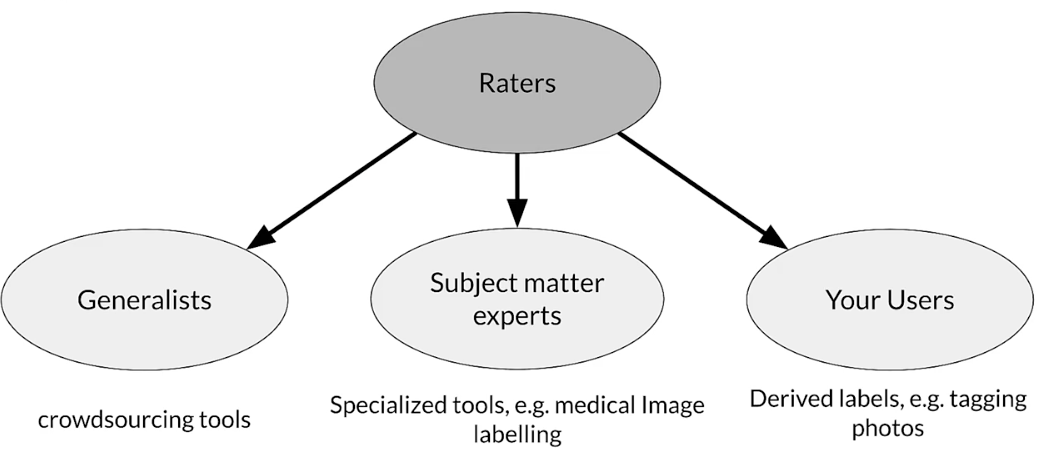
Key points
- Ensure raters pool diversity
- Investigate rater context and incentives
- Evaluate rater tools
- Manage cost
- Determine freshness requirements
Labeling Data
Case study: taking action
- How to detect problems early on?
- What are the possible causes?
- What can be done to solve these?
What causes problesm?
kinds of problems:
- Slow: drift
- Fast: bad sensor, bad software update
Gradual problems

Sudden problems

Why “understand” the model?
- Mispredictions do not have uniform cost to your business
- The data you have is rarely the data you wish you had
- Model objective is nearly always a proxy for your business objectives
- Some percentage of your customers may have a bad experience
Detecting problems with deployed models
- Data and scope changes
- Monitor models and validate data to find problems early
- Changing ground truth: label new training data
Easy problems
- Ground truth changes slowly (months, years)
- Model retraining driven by:
- Model improvements, better data
- Changes in software and/or systems
- Labeling
- Curated datasets
- Crowed-based
Harder problems
- Ground truth changes faster (weeks)
- Model retraining driven by:
- Declining model performance
- Model improvements, better data
- Changes in software and/or system
- Labeling
- Direct feedback
- Crowd-based
Really hard problems
- Ground truth changes very fast (days, hours, min)
- Model retraining driven by:
- Declining model performance
- Model improvements, better data
- Changes in software and/or system
- Labeling
- Direct feedback
- Weak supervision
Key points
- Model performance decays over time
- Data and concept drift
- Model retraining helps to improve performance
- Data labeling for changing ground truth and scarce labels
Data labeling
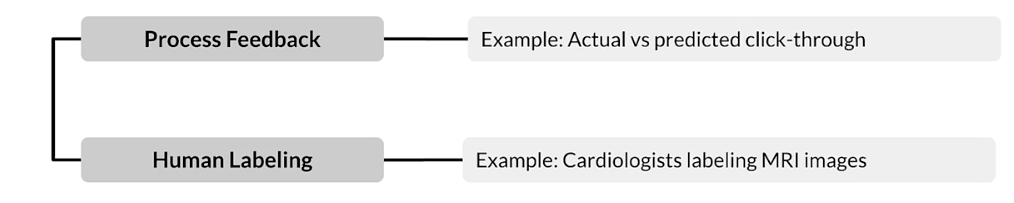
Variety of Methods
- Process Feedback (Direct labeling)
- Human labeling
- Semi-supervised labeling
- Active learning
- Weak supervision
Why is labeling important in production ML?
- using business/organization available data
- Frequent model retraining
- Labeling ongoing and critical process
- Creating a training datasets requires labels
Direct labeling: continuous creation of training dataset
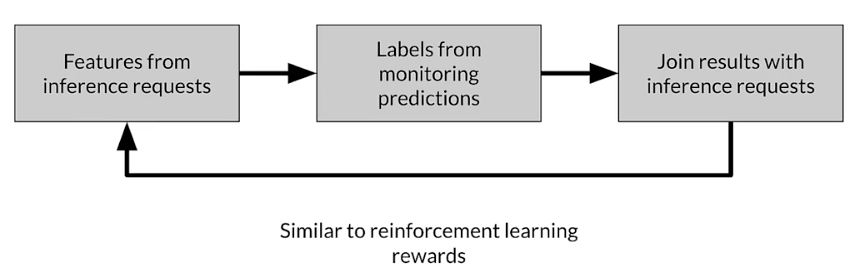
Process feedback - advantages
- Training dataset continuous creation
- Labels evolve quickly
- Captures strong label signals
Process feedback -disadantages
- Hindered by inherent nature of the problem
- Failure to capture ground truth
- Largely bespoke design
Process feedback- Open-source log analysis tools
Logstash: free and open source data processing pipeline
- Ingests data from a multitude of sources
- Transforms it
- Sends it to your favorite “stash”
Fluentd
- Open source data collector
- Unify the data collection and consumption
Process feedback-Cloud log analytics

Human labeling
People (‘raters’) to examine data and assign labels manually
Methodology:
- Unlabeled data is collected
- Human (‘raters’) are recruited
- Instructions to guide raters are created
- Data is divided and assigned to raters
- Labels are collected and conflicts resolved
Human labeling - advantages
- More labels
- Pure supervised learning
Human labeling - disadvantages
- Quality consistency: many datasets difficult for human labeling
- Slow
- Expensive
- Small dataset curation
Validating Data
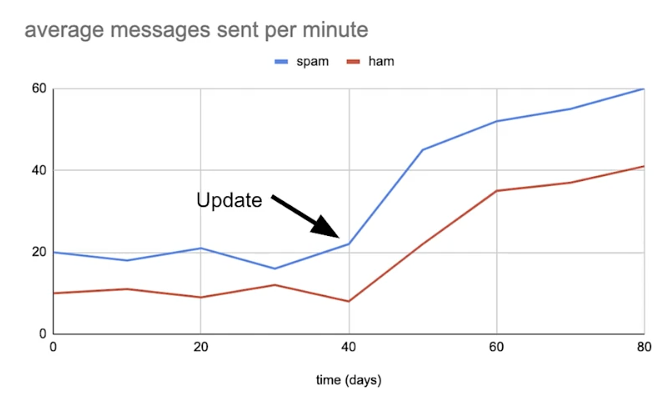
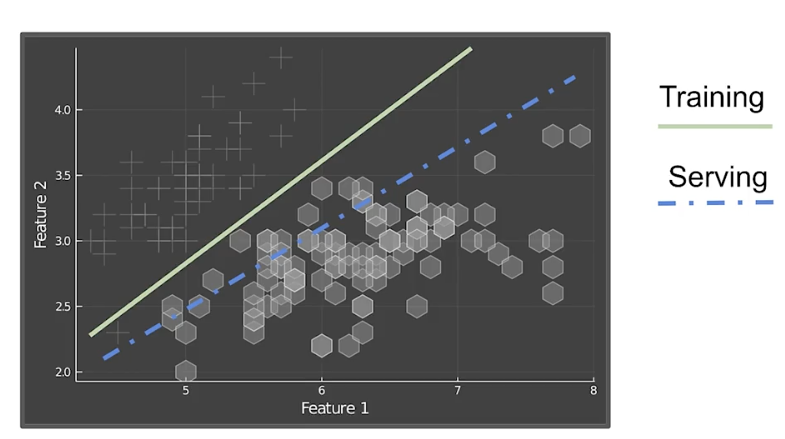
Drift and skew
Drift: changes in data over time, such as data collected once a day
Skew: Difference between two static versions, or different sources, such as training set and serving set
Typical ML pipeline
Model decay: data drift
Performance decay: concept drift
Detecting data issues
- Detecting schema skew
- Training and serving data do not conform to be the same schema
- Detecting distribution skew
- Dataset shift → covariate or concept shift
- Requires continuous evaluation
Detecting distribution skew
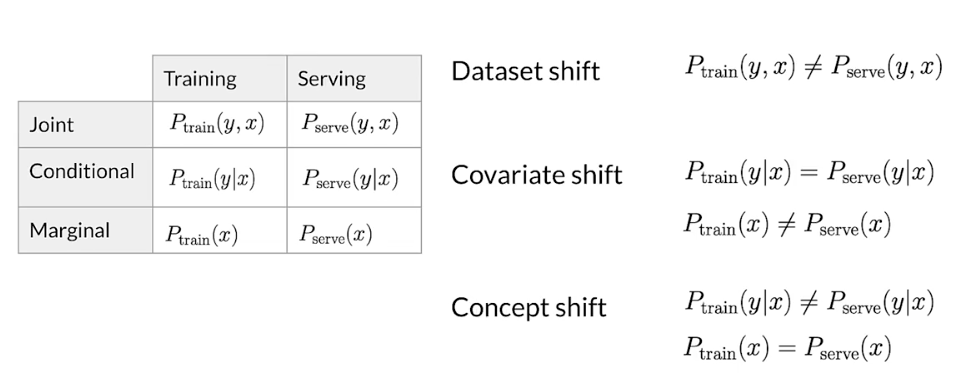
Skew detection workflow
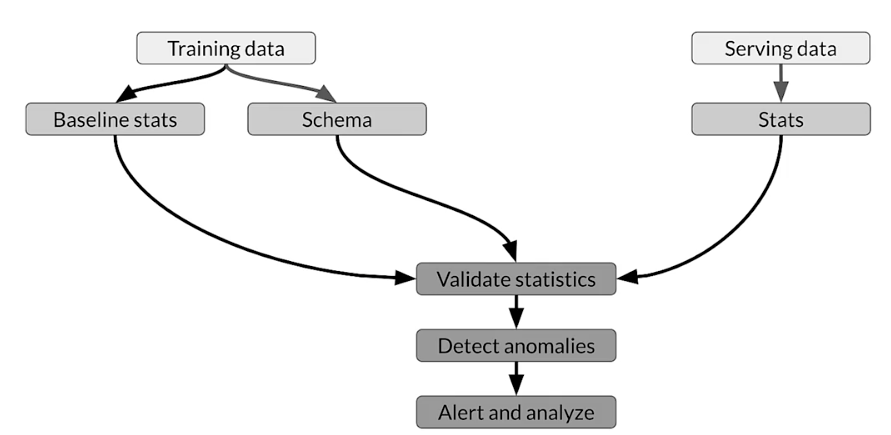
TensorFlow Data Validation (TFDV)
- Understand, validate, and monitor ML data at scale
- Used to analyze and validate petabytes of data at google every day
- Proven track record in helping TFX users maintain the health of their ML pipelines
TFDV capabilities
- Generates data statistics and browser visualizations
- Infers the data schema
- Performs validity checks against schema
- Detects training/serving skew
Skew detection - TFDV
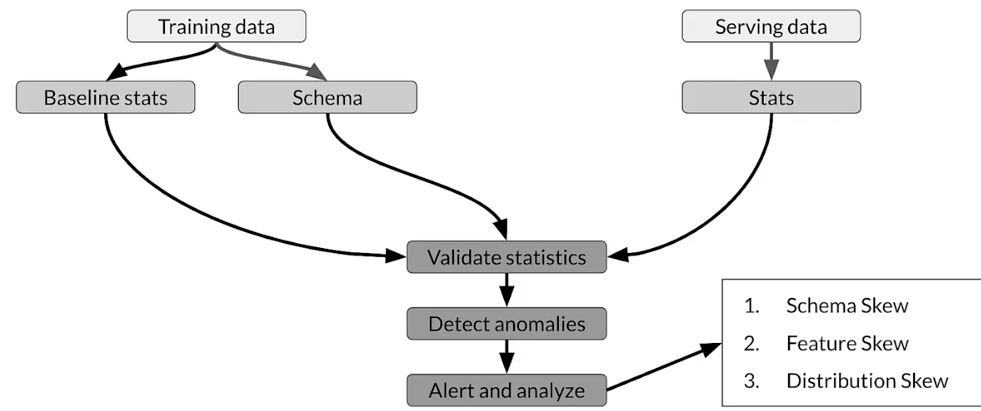
Skew -TFDV
Supported for categorical features
Expressed in terms of L-infinity distance (Chebyshev Distance):
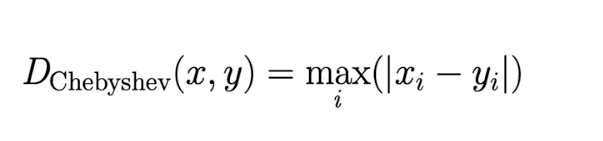
Set a threshold to receive warnings
Schema skew
Serving and training data don’t conform to same schema: int ≠ float
Feature skew
Training feature values are different than the serving feature values:
- Feature values are modified between training and serving time
- Transformation applied only in one of the two instances
Distribution skew
Distribution of serving and training dataset is significantly different:
- Faulty sampling method during training
- Different data sources for training and serving data
- Trend, seasonality, changes in data over time
Key points
- TFDV: descriptive statistics at scale with the embedded facets visualizations
- It provides insight into:
- What are the underlying statistics of your data
- How does your training, evaluation, and serving dataset statistics compare
- How can you detect and fix data anomalies
Readings:
Papers
Konstantinos, Katsiapis, Karmarkar, A., Altay, A., Zaks, A., Polyzotis, N., … Li, Z. (2020). Towards ML Engineering: A brief history of TensorFlow Extended (TFX). http://arxiv.org/abs/2010.02013
Paleyes, A., Urma, R.-G., & Lawrence, N. D. (2020). Challenges in deploying machine learning: A survey of case studies. http://arxiv.org/abs/2011.09926
ML code fraction:
Sculley, D., Holt, G., Golovin, D., Davydov, E., & Phillips, T. (n.d.). Hidden technical debt in machine learning systems. Retrieved April 28, 2021, from Nips.cc https://papers.nips.cc/paper/2015/file/86df7dcfd896fcaf2674f757a2463eba-Paper.pdf
Week 2
Feature Engineering
Squeezing the most out of data
- Making data useful before training a model
- Representing data in forms that help models learn
- Increasing predictive quality
- Reducing dimensionality with feature engineering
Art of feature engineering
Typical ML pipeline
Key points
- Feature engineering can be difficult and time consuming, but also very important to success
- Squeezing the most out of data through feature engineering enables models to learn better
- Concentrating predictive information in fewer features enables more efficient use of compute resources
- Feature engineering during training must also be applied correctly during serving
Main preprocessing operations
Mapping raw data into features
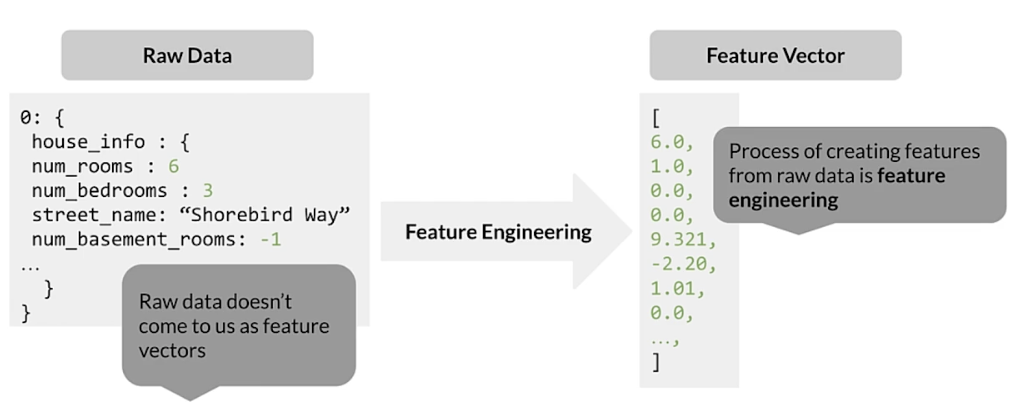
Mapping categorical values
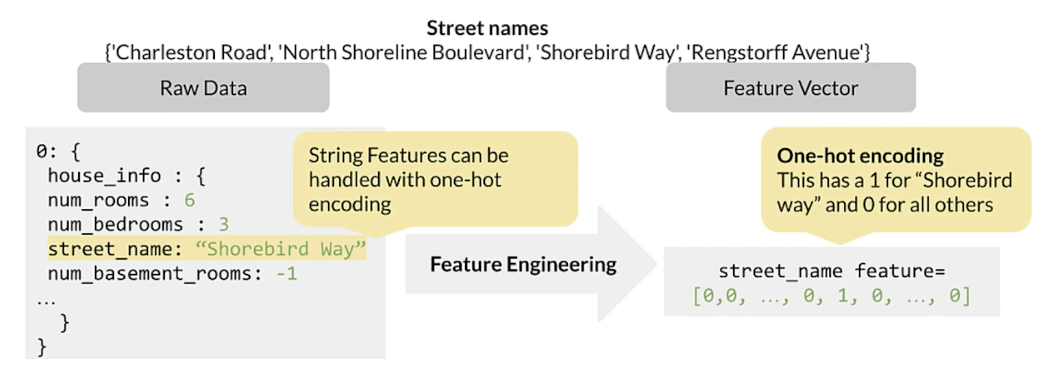
Categorical vocabulary
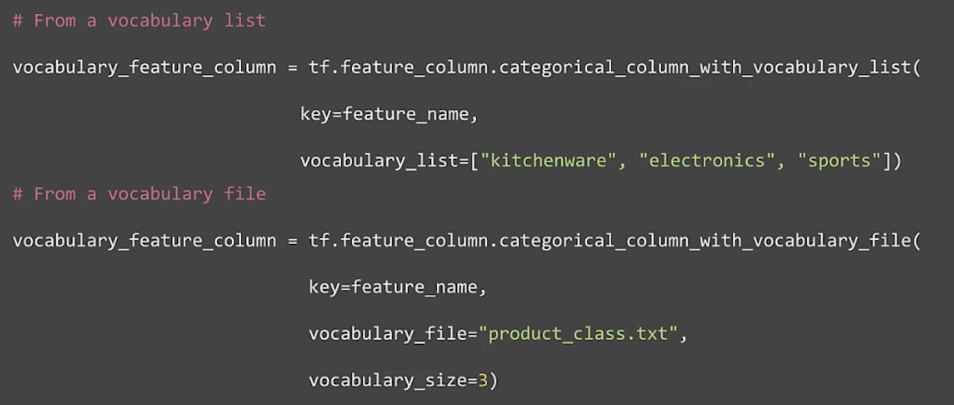
Empirical knowledge of data
- Text: stemming, lemmatization, TF-IDF, n-grams, embedding lookup
- Images: clipping, resizing, cropping, blur, canny filters, Sobel filter, photometric distortions
Key points
- Data preprocessing: transforms raw data into a clean and training-ready dataset
- Feature engineering maps:
- Raw data into feature vectors
- Integer values to floating-point values
- Normalizes numerical values
- Strings and categorical values to vectors of numeric values
- Data from one space into a different space
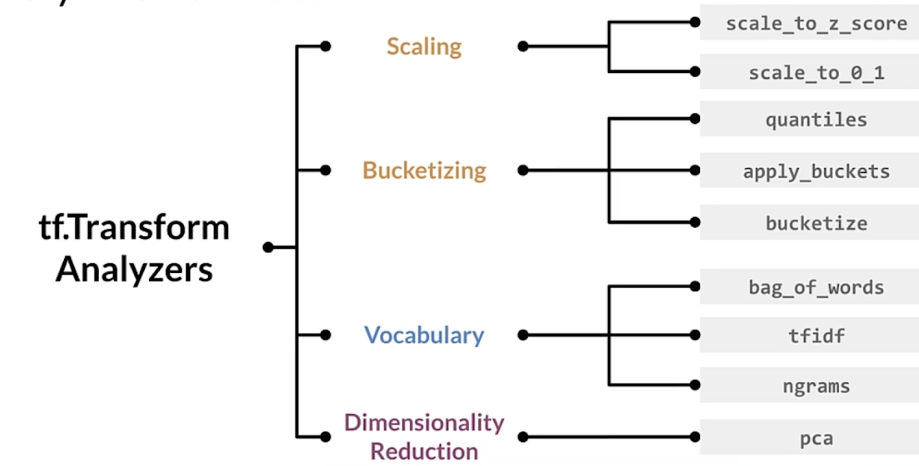
Feature engineering techniques
- Numerical range: scaling, normalizing, standardizing
- Grouping: bucketizing, bag of words
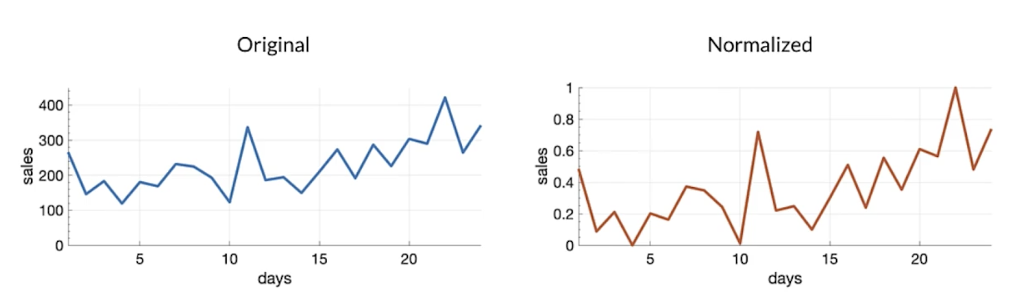
Scaling
- Converts values from their natural range into a prescribed range
- E.g. grayscale image pixel intensity scale is [0,255] usually rescaled to [-1,1]
- Benefits
- Helps neural nets converge faster
- Do away with NaN errors during training
- For each feature, the model learns the right weights
Normalization
If you know the data is not gaussian usually good to do.

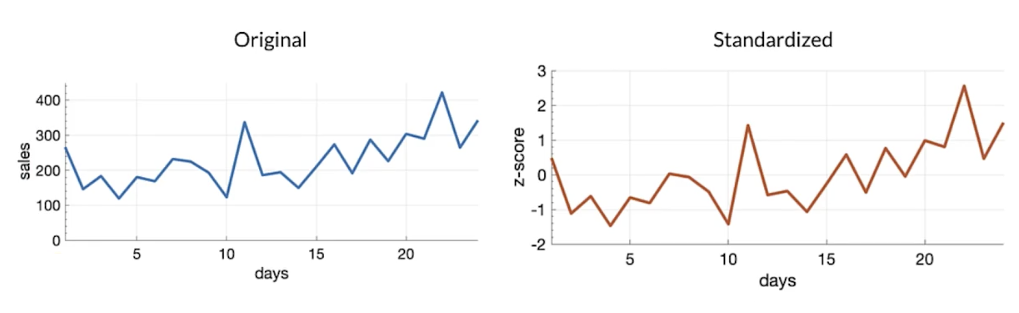
Standardization (z-score)
if your data is normal distribution; try both standardization and normalization.
- Z-score relates the number of standard deviations away from the mean
- e.g.
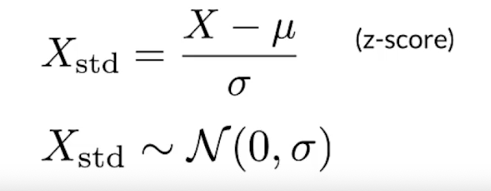
Bucketizing/Binning
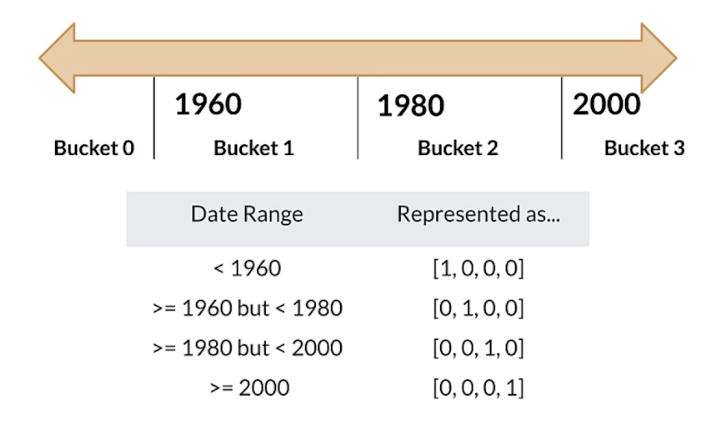
Binning with facets
Other techniques
- Dimensionality reduction in embeddings
- PCA: principal component analysis
- t-SNE: t-Distributed stochastic neighbor embedding (t-SNE)
- UMAP: uniform manifold approximation and projection
- Feature crossing
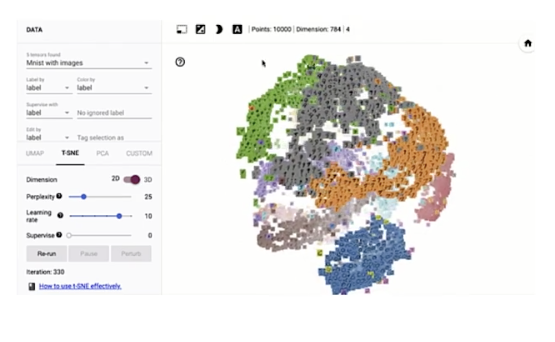
TensorFlow embedding projector
- Intuitive exploration of high-dimensional data
- Visualize and analyze
- Techniques: PCA,t-SNE, UMAP, custom linear projections
Key points
- Feature engineering:
- Prepares, tunes, transforms, extracts, and constructs features.
- Feature engineering is key for model refinement
- Feature engineering helps with ML analysis
Feature crosses
- Combines multiple features together into a new feature
- Encodes nonlinearity in the feature space, or encodes the same information in fewer features
- Create many different kinds of feature crosses
- [A*B]: multiplying the values of two features
- [ABCDE]: multiplying the values of 5 features
- [Day of week, hour]⇒[Hour of week]
Encoding features
can’t be separated by a line
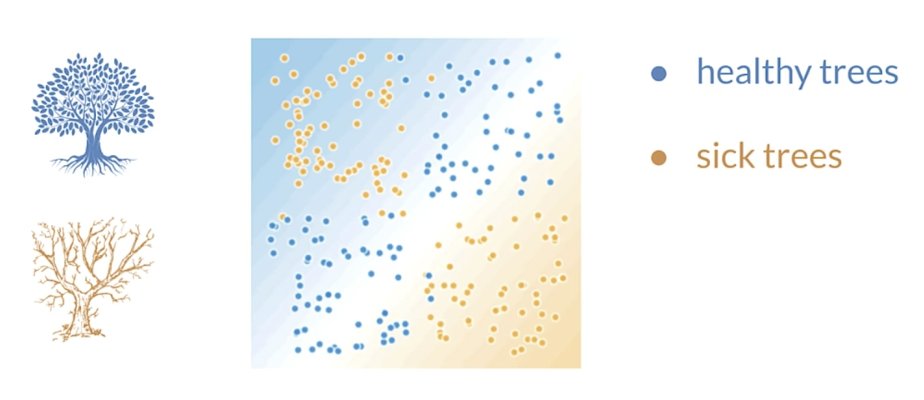
Feature Transformation at Scale
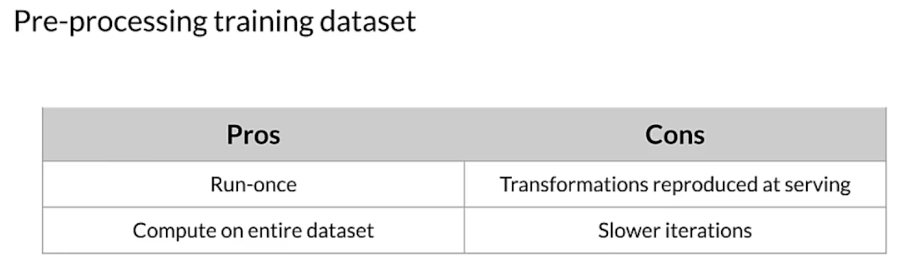
Preprocessing data at scale
- Real-world models: terabytes of data
- Large-scale data processing frameworks
- Consistent transforms between training and serving
Inconsistencies in feature engineering
- Training and serving code paths are different
- Diverse deployments scenarios
- Mobile (TF lite)
- Server (TF serving)
- Web (TF JS)
- Risks of introducing training-serving skews
- Skews will lower the performance of your serving model
Preprocessing granularity
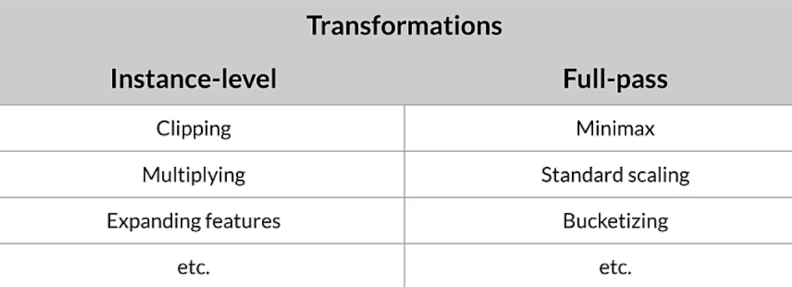
When do you transform?
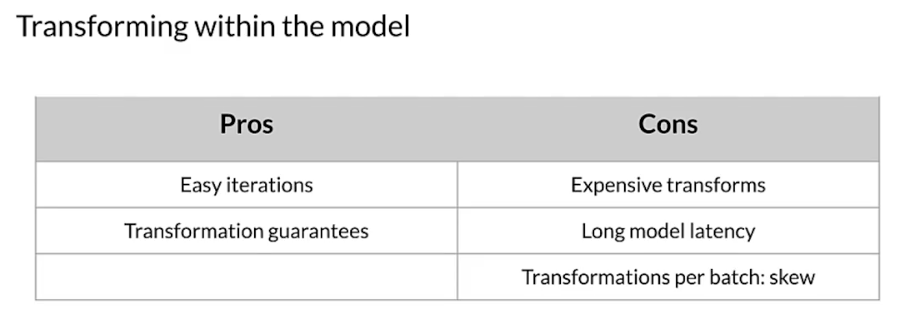
How about ‘within’ a model?
Why transform per batch?
- For example, normalizing features by their average
- Access to a single batch of data, not the full dataset
- Ways to normalize per batch
- Normalize by average within a batch
- Precompute average and reuse it during normalization
Optimizing instance-level transformations
- Indirectly affect training efficiency
- Typically accelerators sit idle while the CPUs transform
- Solution: prefetching transforms for better accelerator efficiency
Summarizing the challenges
- Balancing predictive performance
- Full-pass transformations on training data
- Optimizing instance-level transformations for better training efficiency (GPUs, TPUs,…)
Enter tf.Transform
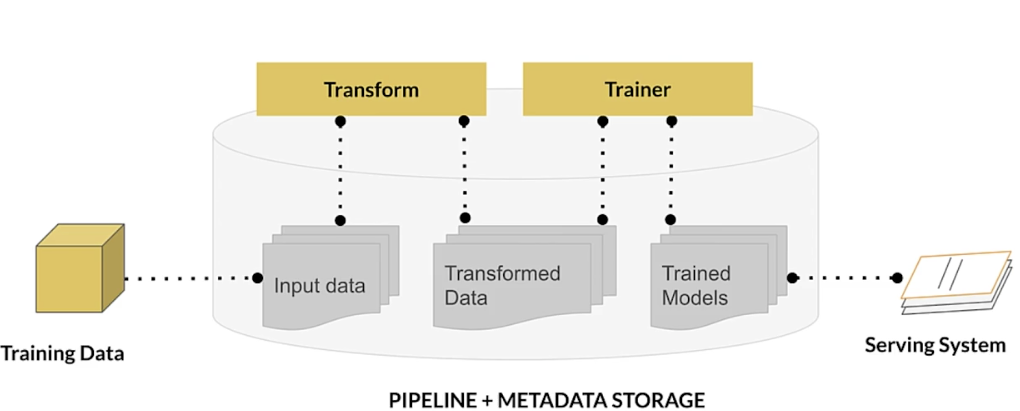
Inside TF Extended
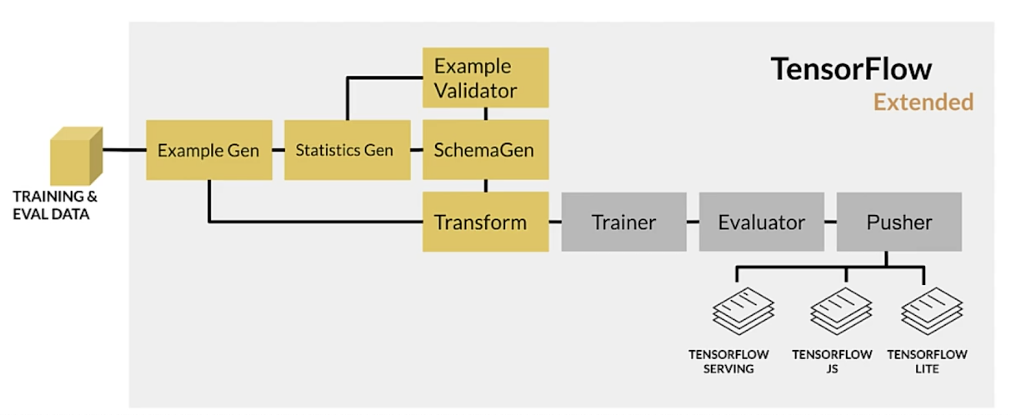
rf.Transform layout
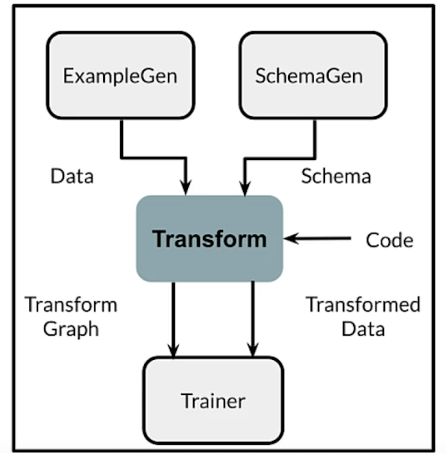
tf.Transform: going deeper
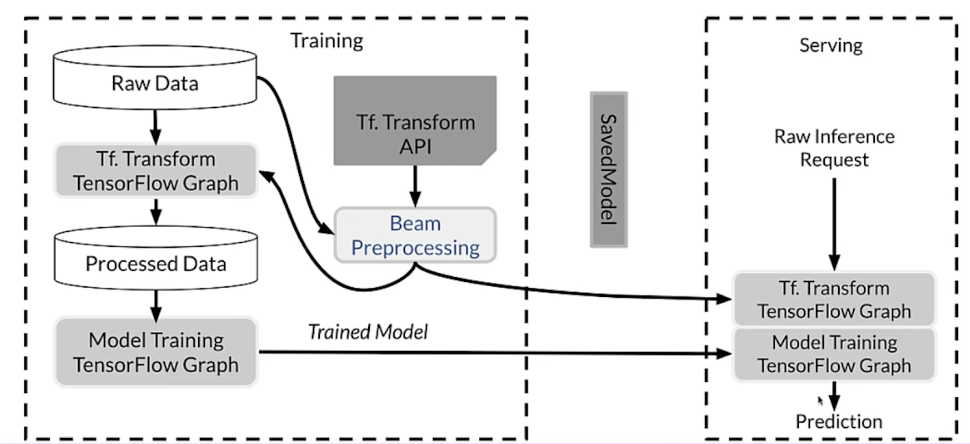
rf.Transform Analyzers

How transform applies feature transformations
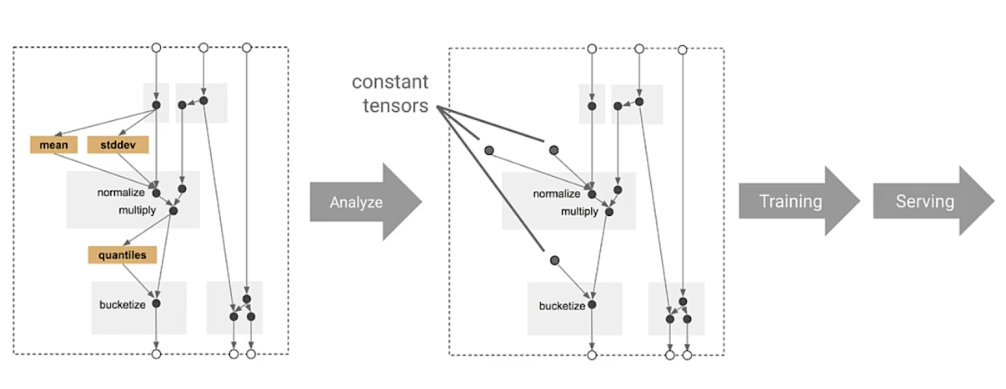
Benefits of using tf.Transform
- Emitted tf.Graph holds all necessary constants and transformations
- Focus on data preprocessing only at training time
- Works in-line during both training and serving
- No need for preprocessing code at serving time
- Consistently applied transformations irrespective of deployment platform
Analyzers framework
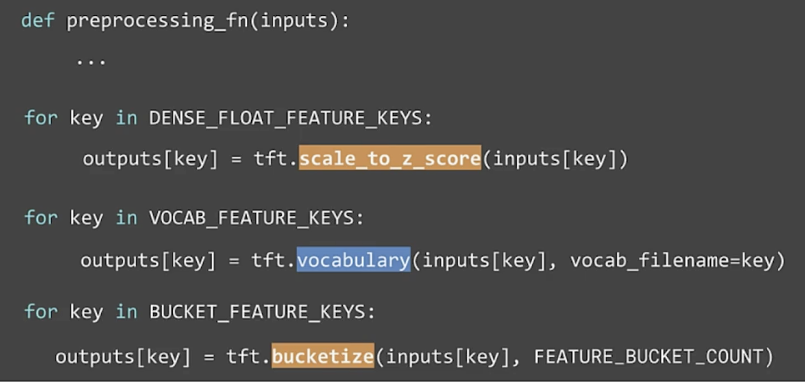
tf.Transform preprocessing_fn
Commonly used imports
Hello world with tf.Transform
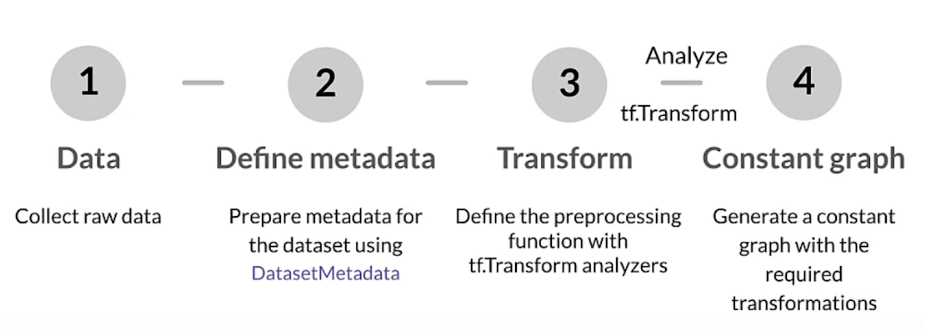
Collect raw samples (data)

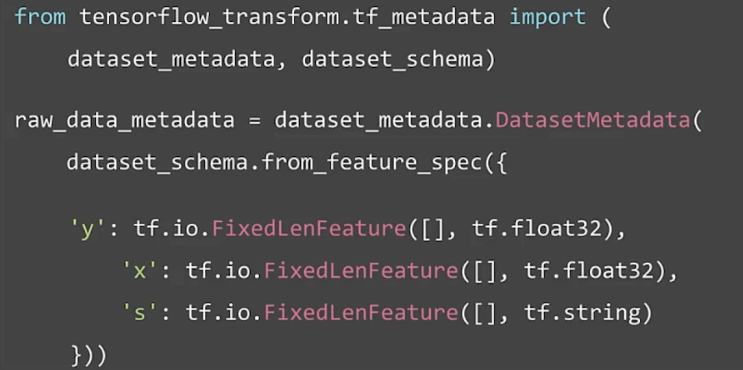
Inspect data and prepare metadata (data)
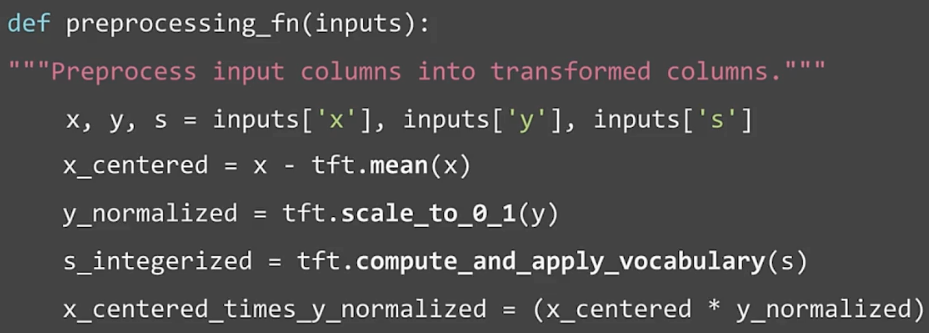
Preprocessing data (transform)

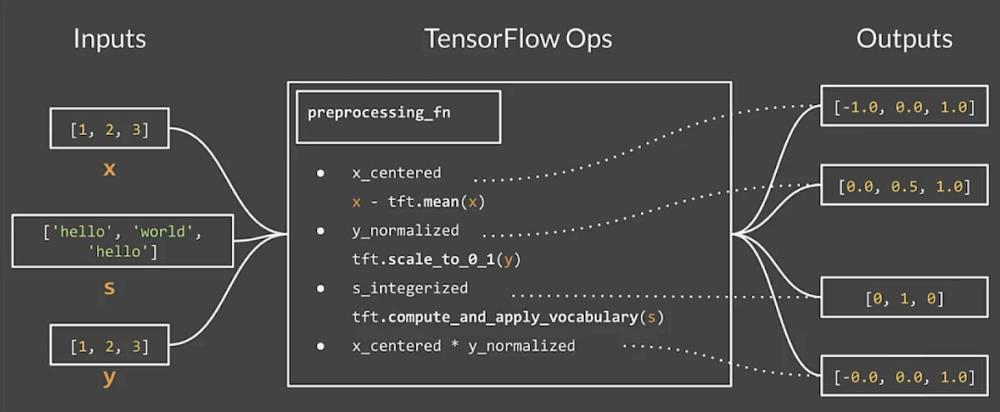
Tensors in…tensors out
Running the pipeline
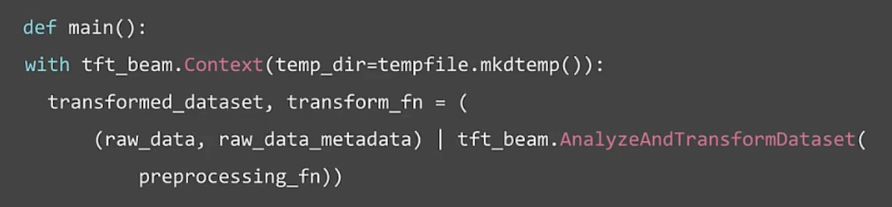
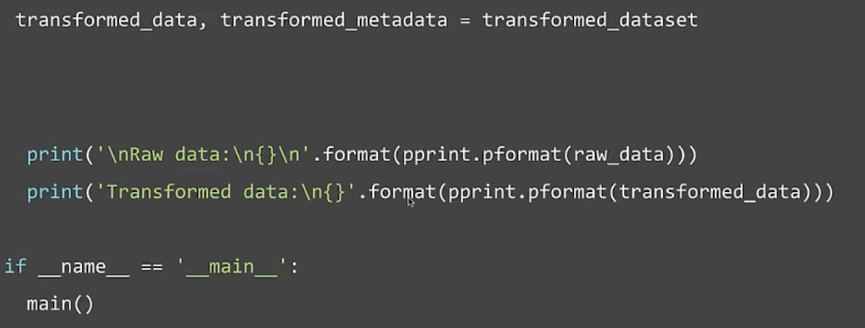
Feature Selection
Feature space
- N dimensional space defined by your N features
- Not including the target label
Feature space coverage
- Train/eval datasets representative of the serving dataset
- same numerical ranges
- same classes
- similar characteristics for image data
- similar vocabulary, syntax, and semantics for NLP problems
Ensure feature space voerage
- Data affected by: seasonality, trend, drift
- Serving data: new values in features and labels
- Continuous monitoring
Feature selection
- Identify features that best represent the relationship
- Remove features that don’t influence the outcome
- Reduce the size of the feature space
- Reduce the resource requirements and model complexity
Why is feature selection needed?
- Reduce storage and I/O requirements
- Minimize training and inference costs
Feature selection methods
- Unsupervised
- Features-target variable relationship not considered
- Removes redundant features (correlation)
- Supervised
- Uses features-target variable relationsihp
- Selects those contributing the most
- Filter methods/Wrapper Methods/Embedded Methods
Filter methods
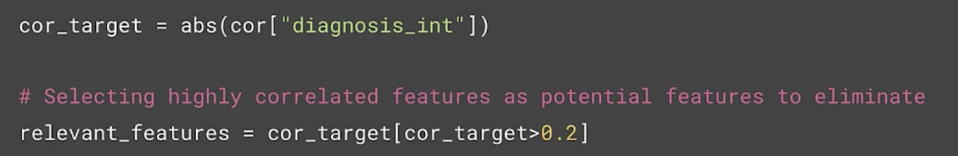
Correlation
Univariate feature selection (for efficiency)
Popular filter methods
- Pearson correlation: between features, and between the features and the label
- Univariate feature selection
Correlation matrix
- Shows how features are related
- To each other (bad)
- And with target variable (good)
- Falls in the range [-1, 1]
Feature comparison statistical tests
- Pearson’s correlation: linear relationships
- Kendall Tau Rank correlation coefficient: monotonic relationships and small sample size
- Spearman’s Rank Correlation Coefficient: monotonic relationships
- Mutual information/F-test/Chi-squared test
Determine correlation

Selecting features
Performance table
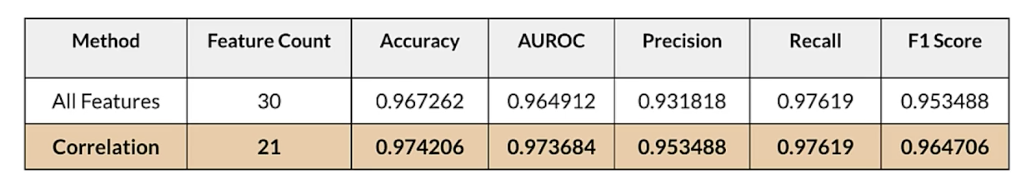
Univariate feature selection in sklearn

Wrapper methods
- Forward elimination
- backward elimination
- recursive feature elimination
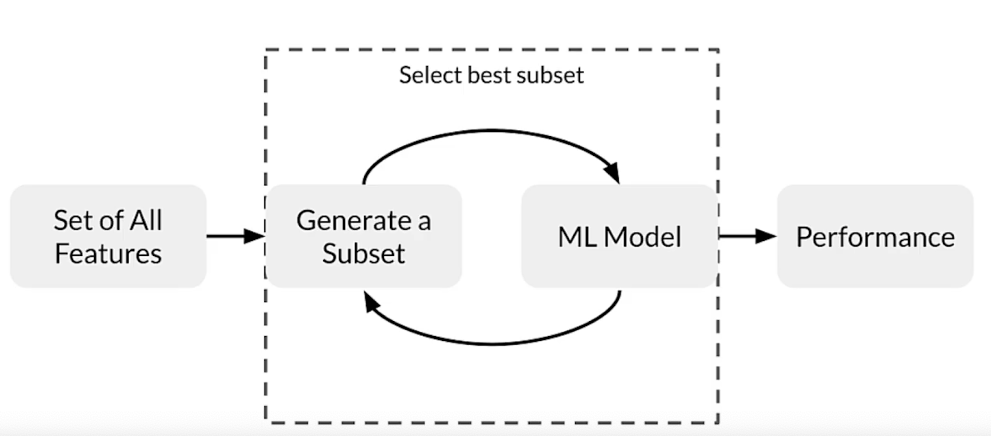
Forward selection
- Iterative, greedy method
- Starts with 1 feature
- Evaluate model performance when adding each of the additional features, one at a time
- Add next feature that gives the best performance
- Repeat until there is no improvement
Backward selection
- Start with all features
- Evaluate model performance when removing each of the included features, one at a time
- Remove next feature that gives the best performance
- Repeat until there is no improvement
Recursive feature elimination (RFE)
- Select a model to use for evaluating feature importance
- Select the desired number of features
- Fit the model
- Rank features by importance
- Discard least important features
- Repeat until the desired number of features remains
Embedded methods
- L1 regularization
- Feature importance
Feature importance
- Assigns scores for each feature in data
- Discard features scored lower by feature importance
Readings
Feature engineering techniques
TFX:
- https://www.tensorflow.org/tfx/guide#tfx_pipelines
- https://ai.googleblog.com/2017/02/preprocessing-for-machine-learning-with.html
Week 3
Data Journey and Data Storage
The data journey
- Raw features and labels
- Input-output map
- ML model to learn mapping
Data transformation
- Data transforms as it flows through the process
- Interpreting model results requires understanding data transformation
Artifacts and the ML pipeline
- Artifacts are created as the components of the ML pipeline execute
- Artifacts include all of the data and objects which are produced by the pipeline components
- This includes the data, in different stages of transformation, the schema, the model itself, metrics, etc.
Data provenance and lineage
- The chain of transformations that led to the creation of a particular artifact
- Important for debugging and reproducibility
Data provenance: why it matters
- Helps with debugging and understanding the ML pipeline:
- Inspect artifacts at each point in the training process
- Trace back through a training run
- Compare training runs
Data lineage: data protection regulation
- Organizations must closely track and organize personal dta
- Data lineage is extremely important for regulatory compliance
Data provenance: interpreting results
- Data transformations sequence leading to predictions
- Understanding the model as it evolves through runs
Data versioning
- Data pipeline management is a major challenge
- machine learning requires reproducibility
- Code versioning: github…
- Environment versioning: docker, terraform, and similar
- Data versioning:
- Version control of datasets
- examples: DVC, Git-LFS
Metadata: tracking artifacts and pipeline changes
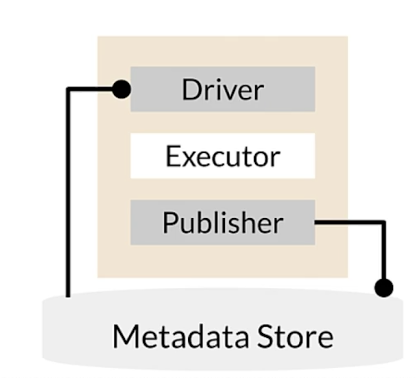
Metadata: TFX component architecture
- Driver: supplies required metadata to executor
- Executor: place to code the functionality of component
- Publisher: stores result into metadata
ML metadata library
- Tracks metadata flowing between components in pipeline
- Supports multiple storage backends
ML metadata terminology
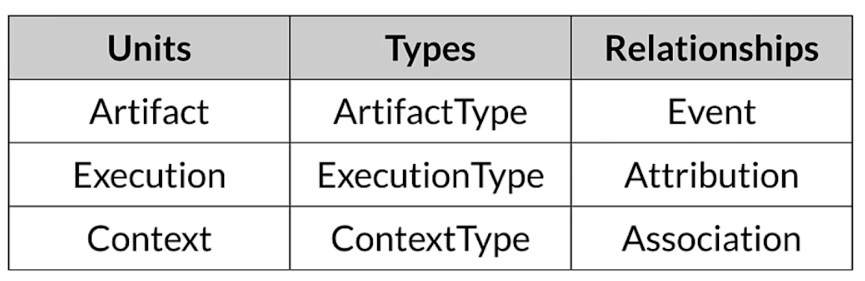
Metadata stored
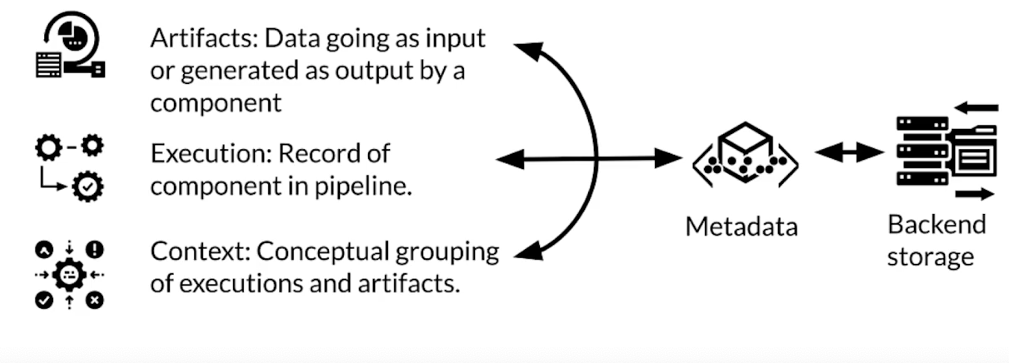
Inside metadatastore
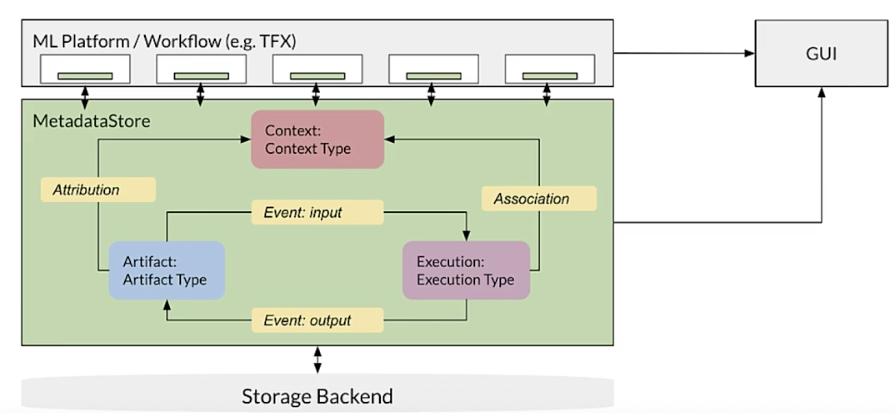
Other benefits of ML Metadata
- Produce DAG of pipelines
- Verify the inputs used in a nexecution
- List all artifacts
- Compare artifacts
ML Metadata storage backend
- ML metadata registers metadata in a database called metadata store
- APIs to record and retrieve metadata to and from the storage backend:
- Fake database: in-memory for fast experimentation/prototyping
- SQLite: in-memory and disk
- MySQL: server based
- Block storage: file system, storage area network, or cloud based
Evolving Data
Recall schema
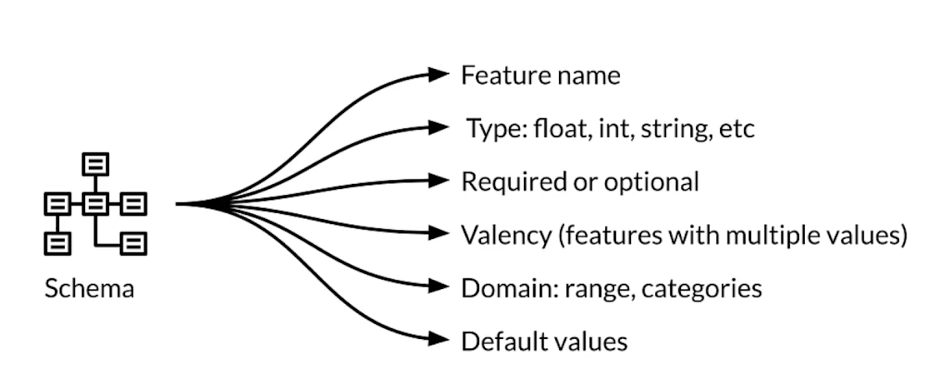
Iterative schema development and evolution
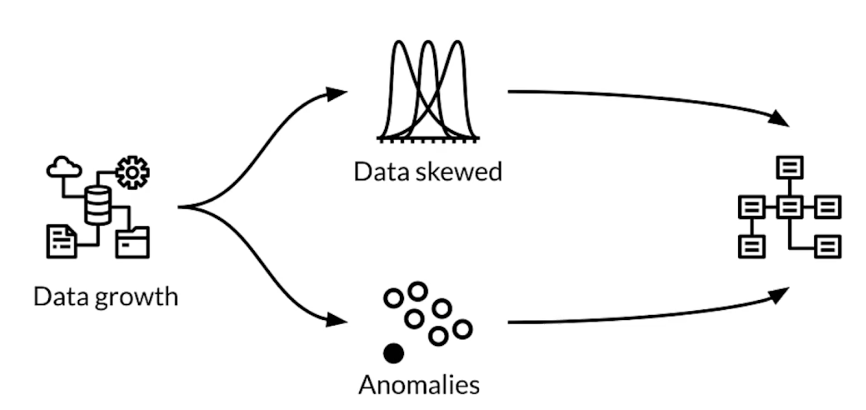
Reliability during data evolution
Platform needs to be resilient to disruptions from:
- Inconsistent data
- Software
- User configurations
- Execution environments
Scalability during data evolution
Platform must scale during:
- High data volume during training
- Variable request traffic during serving
Anomaly detection during data evolution
Platform designed with these principles:
- easy to detect anomalies
- data errors treated same as code bugs
- Updata data schema
Schema inspection during data evolution
- Looking at schema versions to track data evolution
- Schema can drive other automated processes
Multiple schema versions
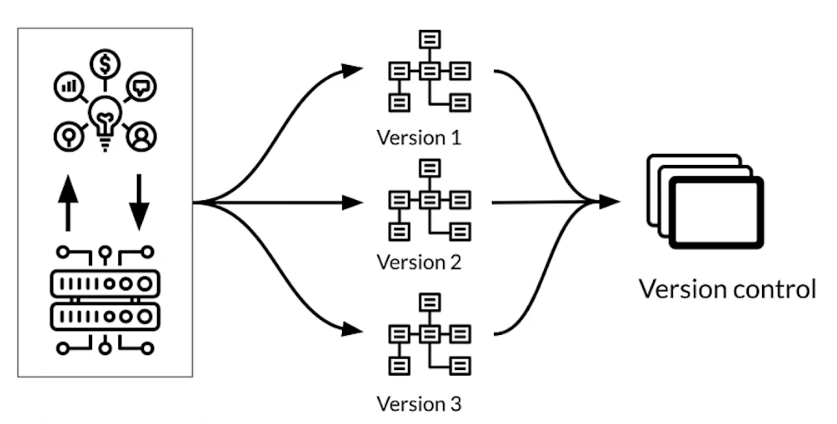
Maintaining varieties of schema
- business use-case needs to support data from different sources
- Data evolves rapidly
- Is anomaly part of accepted type of data
Schema environments
- Customize the schema for each environment
- Ex: add or remove label in schema based on type of dataset
Enterprise Data Storage
Feature stores
Many modeling problems use identical or similar features
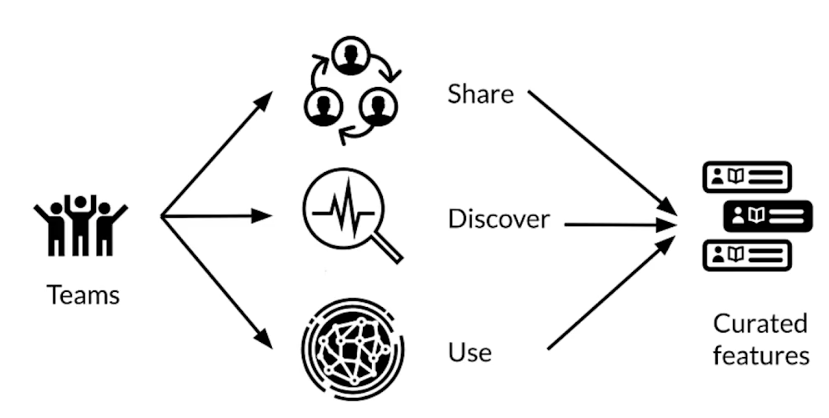

- avoid duplication
- control access
- purge
Offline feature processing
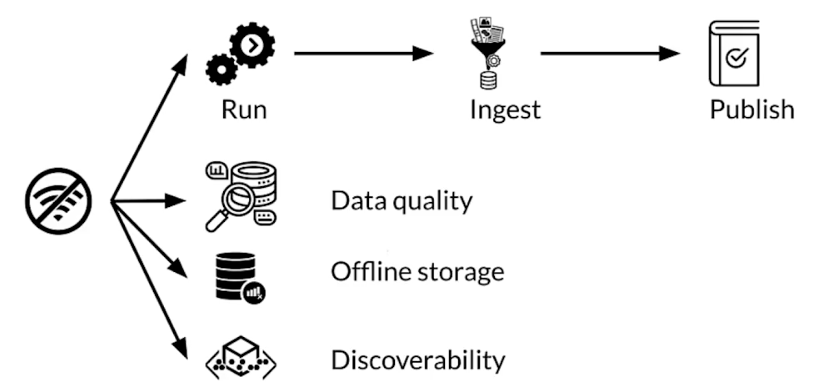
Online feature usage
- Low latency access to features
- Features difficult to compute online
- Precompute and store for low latency access
Features for online serving: batch
Batch precomputing and loading history
- Simple and efficient
- Works well for features to only be updated every few hours or once a day
- Same data is used for training and serving
Feature store: key aspects
- managing feature data from a single person to large enterprises
- Scalable and performant access to feature data in training and servign
- Provide consistent and point-in-time correct access to feature data
- Enable discovery, documentation, and insights into your features
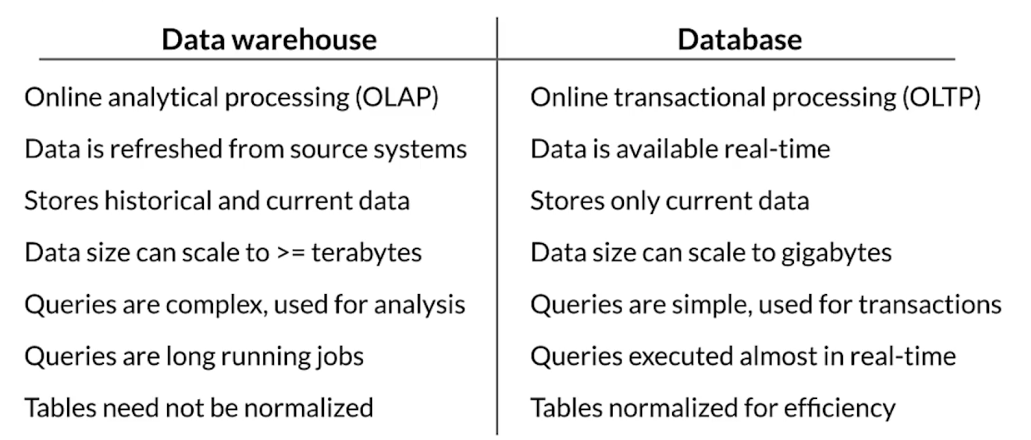
Data warehouse
- Aggregates data sources
- Processed and analyzed
- read optimized
- Not real time
- Follows schema
Key features of data warehouse
- Subject oriented
- Integrated
- Non volatile
- time variant
Advantages of data warehouse
- Enhanced ability to analyze data
- Timely access to data
- Enhanced data quality and consistency
- High return on investment
- Increased query and system performance
Comparison with databases
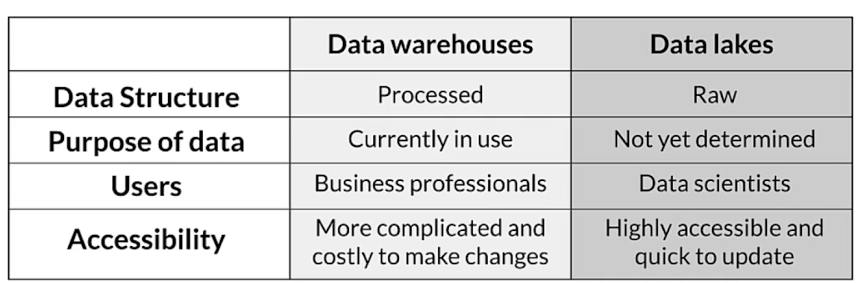
Data lakes
- Aggregates raw data from one or more sources
- Data can be structured or unstructured
- Doesn’t involve any processing before writing data
Comparison with data warehouse
Key points
- Feature store: central repository for storing documented, curated, and access-controlled features, specifically for ML
- Data warehouse: subject-oriented repository of structured data optimized for fast read
- Data Lakes: repository of data stored in its natural and raw format
Reading
If you wish to dive more deeply into the topics covered this week, feel free to check out these optional references. You won’t have to read these to complete this week’s practice quizzes.
Data Versioning:
ML Metadata:
- https://www.tensorflow.org/tfx/guide/mlmd#data_model
- https://www.tensorflow.org/tfx/guide/understanding_custom_components
Chicago taxi trips data set:
- https://data.cityofchicago.org/Transportation/Taxi-Trips/wrvz-psew/data
- https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/covertype
Feast:
- https://cloud.google.com/blog/products/ai-machine-learning/introducing-feast-an-open-source-feature-store-for-machine-learning
- https://github.com/feast-dev/feast
- https://blog.gojekengineering.com/feast-bridging-ml-models-and-data-efd06b7d1644
Week 4
Advanced Labeling
Why is advanced labeling important
- manually labeling of data is expensive
- Unlabeled data is usually cheap and easy to get
- Unlabeled data contains a lot of information that can improve our model
Semi-supervised learning
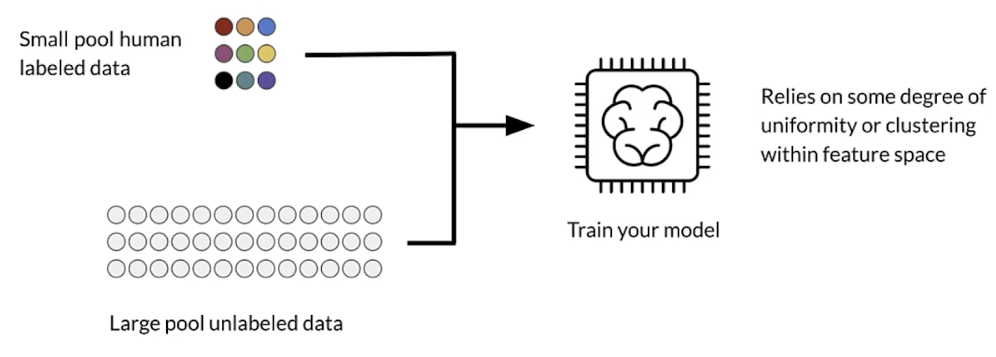
- Advantages
- Combining labeled and unlabeled data boosts accuracy
- Getting unlabeled data is cheap
Label propagation
- Semi-supervised ML algorithm
- A subset of the examples have labels
- Labels are propagated to the unlabeled points:
- Based on similarity of “community structure”
Label propagation - graph based
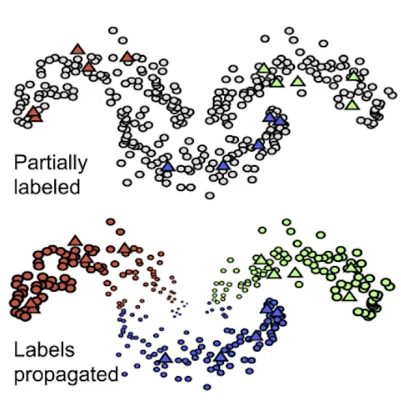
- Unlabeled examples can be assigned labels based on their neighbors
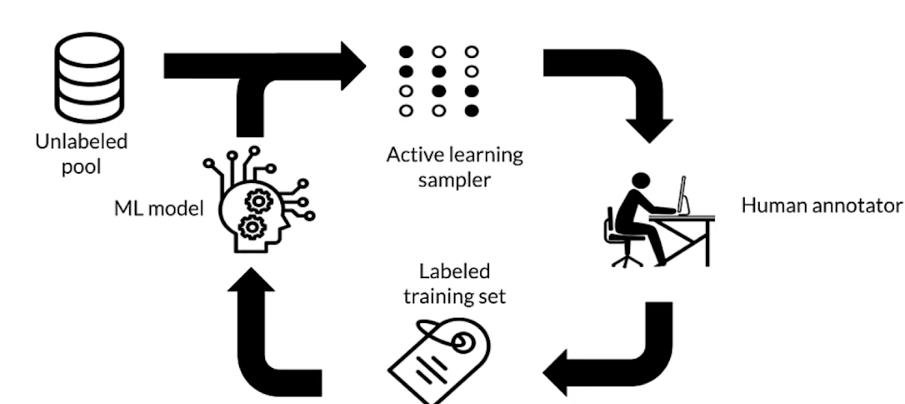
Active learning
- A family of algorithms for intelligently sampling data
- Select the points to be labeled that would be most informative for model training
- Very helpful in the following situations:
- Constrained data budgets: you can only afford labeling a few points
- Imbalanced dataset: helps selecting rare classes for training
- Target metrics: when baseline sampling strategy does not improve selected metrics
Active learning strategies
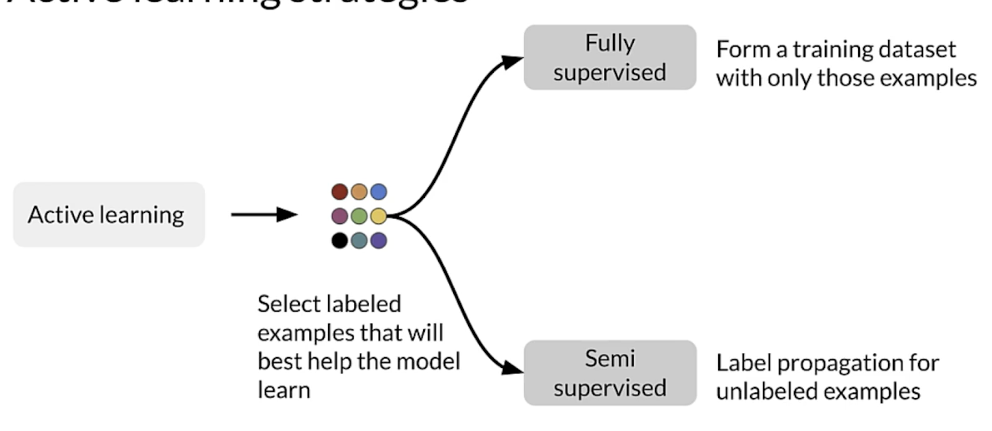
Active learning cycle
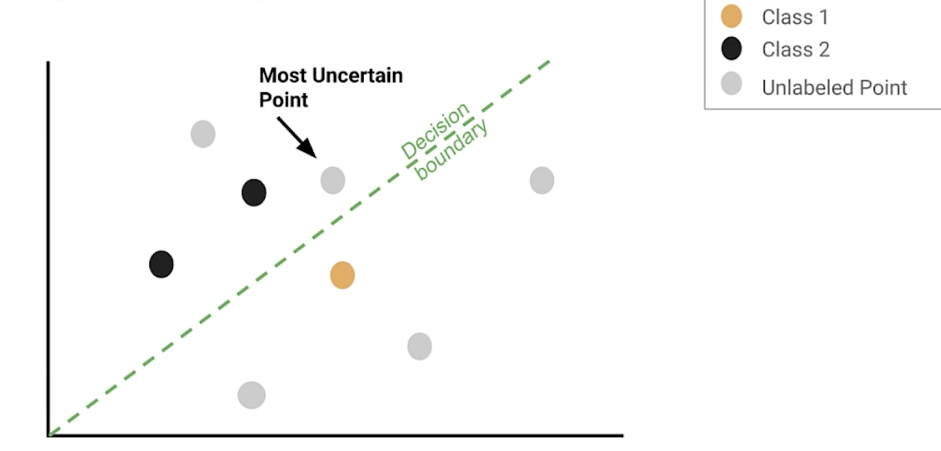
Margin sampling
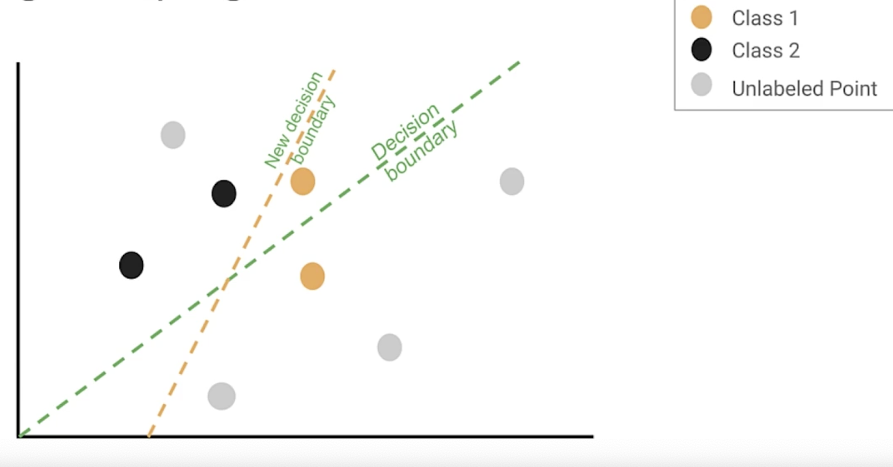
repeat until the performance doesn’t improve
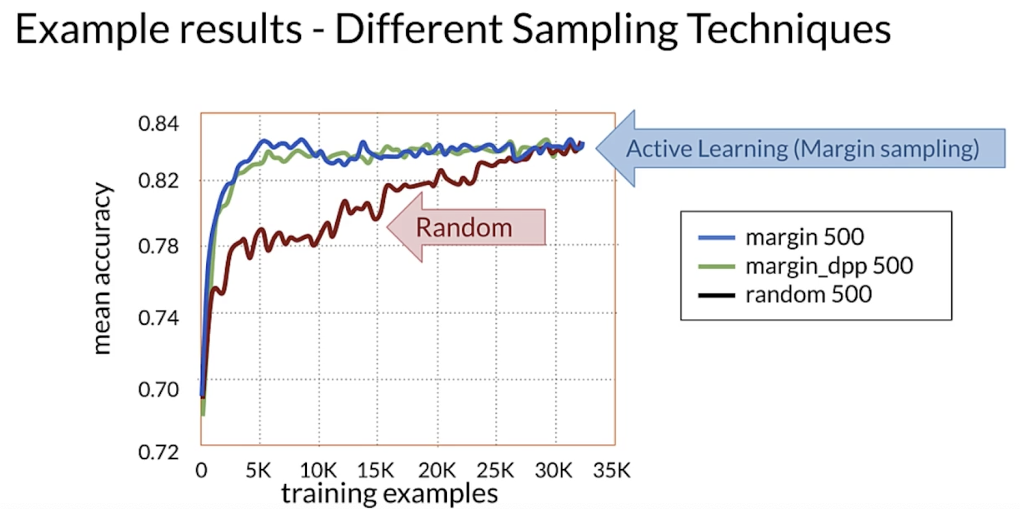
Active learning sampling techniques
- Margin sampling: label points the current model is least confident in
- Cluster-based sampling: sample from well-formed clusters to ‘cover’ the entire space
- Query-by-committee: train an ensemble of models and sample points that generate disagreement
- Region-based sampling: runs several active learning algorithms in different partitions of the space
Weak supervision
Weak supervision is about leveraging higher-level and/or noisier input from subject matter experts.
- Unlabeled data, without ground-truth labels
- One or more weak supervision sources
- a list of heuristics that can automate labeling
- Typically provided by subject matter experts
- Noisy labels have a certain probability of being correct, not 100%
- Objective: learn a generative model to determine weights for weak supervision sources
Snorkel
- Programmatically building and managing training datasets without manual labeling
- Automatically: models, cleans, and integrates the resulting training data
- Applies novel, theoretically-grounded techniques
- Also offers data augmentation and slicing
Data programming pipeline in Snorkel
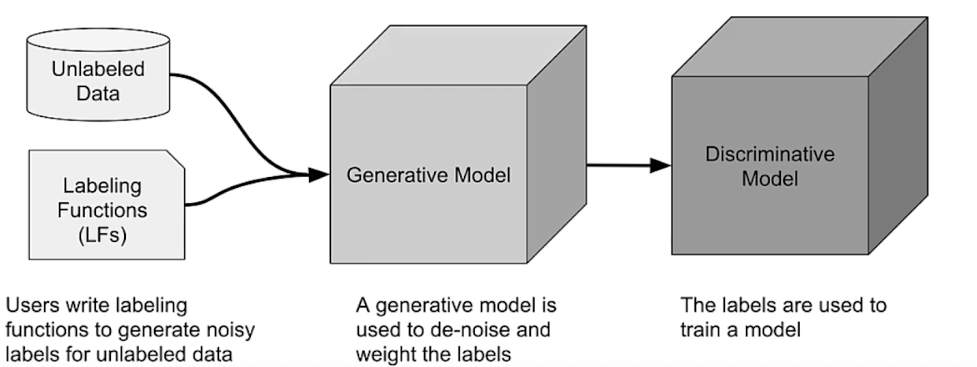
Data Augmentation
How do you get more data?
- Augmentation as a way to expand datasets
- One way is introducing minor alterations
- For images: flips, rotations, etc
How does augmentation data help?
- Adds examples that are similar to real examples
- Improves coverage of feature space
- Beware of invalid augmentations
Other advanced techniques
- Semi-supervised data augmentation. e.g., UDA, semi-supervised learning with GANs
- Policy-based data augmentation e.g., AutoAugment

Preprocessing Different Data Types
Different types of data
- TRX pre-processing capabilities for multiple data types
- Images
- Video
- text
- audio
- time series
Time series data
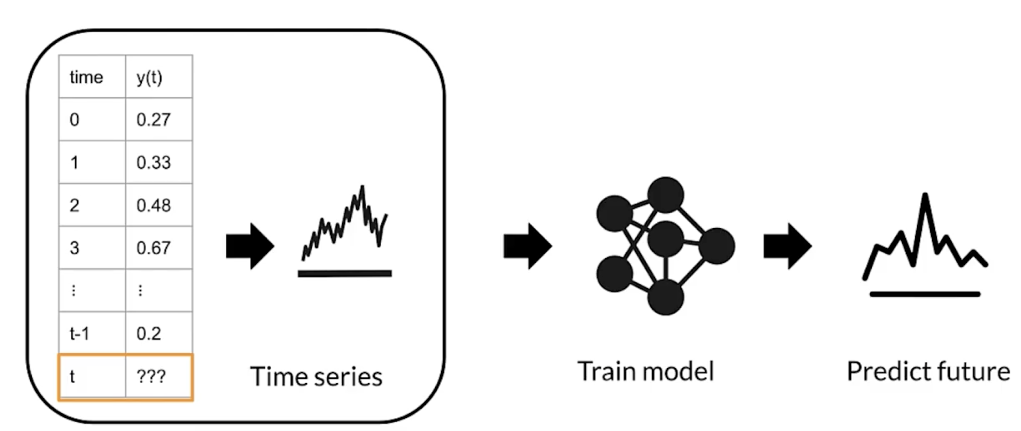
Time series forecasting
- predicts future events by analyzing data from the past
- makes predictions on data indexed by time
- example:
- predict future temperature at a given location based on historical meteorological data
Time series dataset: weather prediction
- to preprocess time series data with tensorflow transform
- to convert data int sequences of time steps
- making data ready to train a long short-term memory recurrent neural network
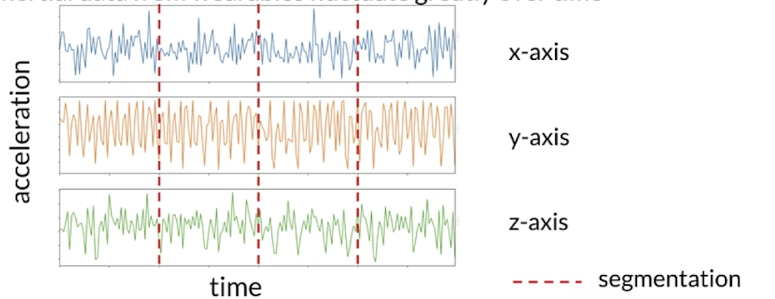
Sensors and signals
- Signals are sequences of data collected from real time sensors
- Each data point is indexed by a timestamp
- Sensors and signals data is thus time series data
- Example: classify sequences of accelerometer data recorded by the sensors on smartphones to identify the associate activity
Human activity recognition
HAR tasks require segmentation operations
- Raw inertial data from wearables fluctuate greatly over time
- Segmented data should be transformed for modeling
- Different methods of transformation:
- Spectrograms
- normalization end encoding
- Multichannel
- Fourier transform
Reading
CIFAR-10
Papers
Label Propagation:
Iscen, A., Tolias, G., Avrithis, Y., & Chum, O. (2019). Label propagation for deep semi-supervised learning. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1904.04717.pdf
Slide 13 active learning:
Source: Original slides by Yale Cong